Navigating the Terrain of Artificial Intelligence: Harnessing the Power, Acknowledging the Perils
Introduction:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force, revolutionizing industries and reshaping the way we live, work, and interact. This powerful technology, driven by machine learning algorithms and data analytics, holds immense promise, yet it is not without its challenges. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the essence of AI, its myriad advantages, the lurking disadvantages, and the imperative to wield this technological prowess wisely.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence:
At its core, AI refers to the development of computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and language understanding. Unlike traditional computer programs that follow predefined rules, AI systems can adapt and improve their performance over time as they encounter more data.
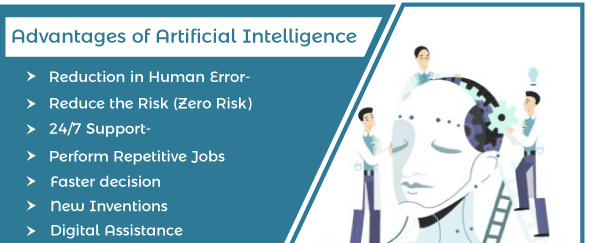
Advantages of AI:
1. Efficiency and Automation:
AI excels at automating repetitive and mundane tasks, liberating human resources for more complex and creative endeavors. Industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and customer service have witnessed significant efficiency gains through the implementation of AI-powered automation.
2. Data Analysis and Insights:
The ability of AI to process vast amounts of data at incredible speeds enables organizations to extract valuable insights. This data-driven decision-making enhances strategic planning, marketing strategies, and overall business intelligence.
3. Personalization:
AI facilitates personalized experiences, from tailored product recommendations in e-commerce to personalized learning paths in education. This individualization not only enhances user satisfaction but also contributes to increased efficiency in various domains.
4. Medical Breakthroughs:
In the healthcare sector, AI has demonstrated remarkable capabilities in diagnosing diseases, analyzing medical images, and even predicting patient outcomes. These applications contribute to early detection, more accurate diagnoses, and improved treatment plans.
5. Innovation and Creativity:
AI serves as a catalyst for innovation, enabling the development of new technologies and solutions. From self-driving cars to virtual assistants, AI has sparked creativity across diverse fields, pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
Disadvantages of AI:
1. Job Displacement:
One of the primary concerns surrounding AI is the potential displacement of jobs due to automation. Routine tasks being automated may lead to job losses in certain sectors, necessitating a shift in workforce skills.
2. Bias and Fairness Issues:
AI systems are only as unbiased as the data they are trained on. If the training data contains biases, the AI models may perpetuate and even amplify those biases, leading to unfair and discriminatory outcomes.
3. Security Risks:
The increasing reliance on AI systems introduces new security challenges. Malicious actors could exploit vulnerabilities in AI algorithms, leading to data breaches, identity theft, or even the manipulation of AI systems for nefarious purposes.
4. Ethical Dilemmas:
AI raises complex ethical questions, especially in areas such as autonomous weapons, surveillance, and privacy. Determining the ethical boundaries of AI development and use requires careful consideration and global collaboration.
5. Lack of Understanding:
The intricate nature of AI systems makes them challenging to understand for non-experts. This lack of transparency can lead to distrust and hinder widespread adoption, as users may be skeptical about the decisions made by AI algorithms.
Using AI Wisely:
1.Ethical AI Development:
Developers must prioritize ethical considerations throughout the AI development process. This includes addressing biases in training data, ensuring transparency in algorithms, and establishing clear guidelines for responsible AI use.
2. Human-AI Collaboration:
Rather than viewing AI as a replacement for human capabilities, it should be seen as a tool to augment human potential. Emphasizing collaboration between humans and AI can lead to more effective and beneficial outcomes.
3. Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation:
Regular monitoring and evaluation of AI systems are crucial to identify and rectify issues promptly. This includes ongoing assessments of fairness, security, and ethical implications to ensure responsible AI deployment.
4. Investment in Education and Skills:
As AI reshapes the job market, there is a need for continuous education and upskilling. Governments, businesses, and educational institutions should collaborate to provide training programs that equip individuals with the skills needed in the AI-driven economy.
5. Global Collaboration and Regulation:
Given the cross-border nature of AI, international collaboration and the establishment of clear regulations are imperative. Shared standards can help mitigate risks and ensure that AI is developed and used responsibly on a global scale.
Conclusion:
Artificial Intelligence is a double-edged sword, offering immense possibilities while posing substantial challenges. Recognizing the advantages, understanding the disadvantages, and using AI wisely are critical steps in navigating the complex terrain of this transformative technology. As we journey further into the era of AI, the responsibility lies with developers, policymakers, and society as a whole to harness its power for the greater good, ensuring a future where AI enhances humanity rather than replaces it.



Comments
Post a Comment